Pipeline Management is the strategic process of overseeing the flow of work from its initial stages to completion, ensuring efficiency, effectiveness, and ultimately, success. It’s a critical component of various industries, including manufacturing, software development, and marketing, where managing the flow of tasks, resources, and information is essential for achieving desired outcomes.
Understanding the principles and objectives of pipeline management is crucial for organizations aiming to streamline their operations, reduce bottlenecks, and maximize productivity. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of pipeline management, including its stages, tools, techniques, challenges, and future trends, providing insights into best practices and real-world applications.
What is Pipeline Management?
Pipeline management is a crucial process in various industries, encompassing the planning, execution, and monitoring of projects or tasks through different stages, from initiation to completion. It involves managing a flow of activities or resources, ensuring that each stage is completed efficiently and effectively.
The Significance of Pipeline Management
Effective pipeline management is vital for businesses across diverse industries, including technology, manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. It plays a crucial role in optimizing resource allocation, enhancing productivity, and achieving business goals.
- Improved resource allocation:Pipeline management enables businesses to allocate resources strategically, ensuring that the right resources are available at the right time for each stage of a project or task. This minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency.
- Enhanced productivity:By streamlining workflows and eliminating bottlenecks, pipeline management enhances overall productivity. It helps teams stay focused and on track, reducing delays and improving time-to-market.
- Increased visibility and control:Pipeline management provides a clear view of the progress of projects and tasks, allowing businesses to track progress, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions. This empowers organizations to maintain control over their operations and proactively address challenges.
Core Principles and Objectives, Pipeline Management
Pipeline management adheres to specific principles and objectives that guide its implementation and effectiveness.
- Define clear goals and objectives:Every pipeline should have well-defined goals and objectives that align with the overall business strategy. This ensures that all efforts are directed towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Establish a structured process:A well-defined process for managing the pipeline is essential. This involves defining stages, assigning responsibilities, and setting clear timelines for each stage.
- Prioritize and manage tasks:Effective pipeline management requires prioritizing tasks based on their importance and urgency. This ensures that critical activities are addressed first and resources are allocated efficiently.
- Regular monitoring and evaluation:Continuous monitoring and evaluation are crucial to ensure that the pipeline is on track and adjustments are made as needed. This involves tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing corrective measures.
Types of Pipelines and Management Challenges
Different industries and organizations utilize various types of pipelines, each with its unique management challenges.
- Sales pipeline:This pipeline tracks the progress of potential customers through different stages, from lead generation to closing deals. Management challenges include identifying qualified leads, nurturing relationships, and overcoming objections.
- Product development pipeline:This pipeline manages the development of new products, from ideation to launch. Management challenges include managing complex dependencies, ensuring quality, and meeting deadlines.
- Project pipeline:This pipeline tracks the progress of multiple projects, from initiation to completion. Management challenges include allocating resources effectively, managing dependencies between projects, and ensuring alignment with business goals.
Stages of a Pipeline
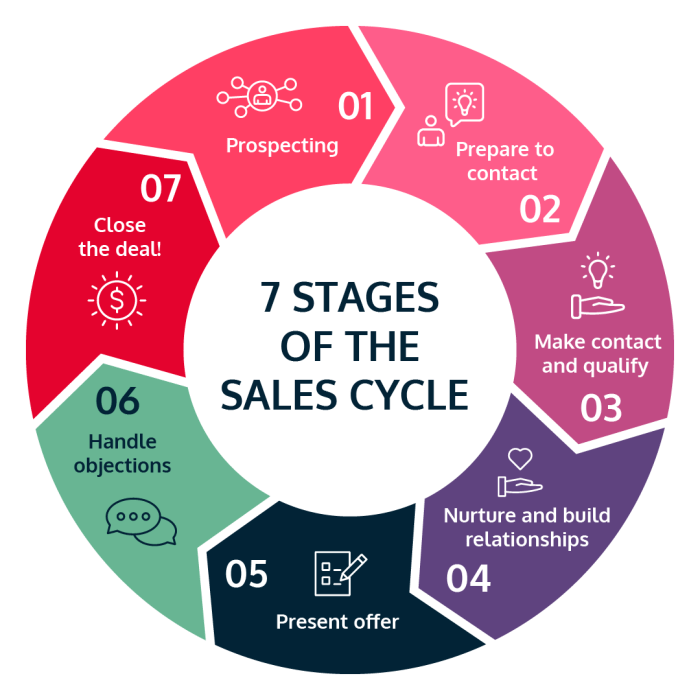
A sales pipeline is a visual representation of the journey a prospect takes from initial contact to becoming a paying customer. It’s a roadmap that helps sales teams track progress, identify bottlenecks, and optimize their efforts to close more deals.
Stages of a Pipeline
The stages of a sales pipeline vary depending on the industry, company size, and complexity of the sales process. However, a typical pipeline includes the following stages:
- Lead Generation: This stage involves identifying and attracting potential customers. It encompasses activities such as marketing campaigns, networking, and cold outreach. Key responsibilities include developing targeted marketing materials, engaging with prospects through various channels, and qualifying leads based on predetermined criteria.
- Qualification: In this stage, sales representatives assess the suitability of leads and determine if they meet the criteria for a potential customer. This involves gathering information about the prospect’s needs, budget, and decision-making process. The key responsibility here is to understand the prospect’s requirements and evaluate their potential for conversion.
- Proposal: This stage involves presenting a tailored solution to the prospect based on their specific needs. It includes creating a compelling proposal that Artikels the benefits of the product or service and addresses any concerns the prospect may have. The key responsibility is to develop a persuasive and value-driven proposal that resonates with the prospect.
- Negotiation: Once a proposal is presented, the negotiation stage begins. This involves discussing the terms of the deal, including pricing, timelines, and deliverables. The key responsibility is to effectively communicate and negotiate to reach a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Closing: This is the final stage where the deal is formally closed. It involves securing a commitment from the prospect and finalizing all necessary paperwork. The key responsibility is to ensure a smooth and efficient closing process, including addressing any last-minute questions or concerns.
- Onboarding: After the deal is closed, the onboarding stage begins. This involves integrating the new customer into the company’s systems and processes, providing necessary training and support. The key responsibility is to ensure a seamless transition for the new customer and set them up for success.
Visual Representation of Pipeline Stages
The following table provides a visual representation of the pipeline stages and their corresponding tasks:
| Stage | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Lead Generation | Marketing campaigns, networking, cold outreach, lead qualification |
| Qualification | Needs assessment, budget evaluation, decision-maker identification |
| Proposal | Solution development, proposal creation, presentation |
| Negotiation | Terms discussion, pricing negotiation, agreement finalization |
| Closing | Commitment securing, paperwork finalization |
| Onboarding | Customer integration, training, support |
Pipeline Management Tools and Techniques

Effective pipeline management relies on a combination of tools, software solutions, and methodologies that streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance the overall efficiency of the sales funnel. These tools and techniques empower businesses to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to maximize conversion rates and achieve sales targets.
Pipeline Management Software Solutions
A wide range of software solutions is available to assist organizations in managing their sales pipelines. These tools offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to simplify and automate various aspects of pipeline management, providing valuable insights and actionable data.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems:CRMs are comprehensive platforms that integrate various functionalities, including sales pipeline management, customer interaction tracking, and marketing automation. They provide a centralized repository for customer data, enabling sales teams to gain a holistic view of their prospects and customers.
Popular CRM systems include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM.
- Sales Pipeline Management Software:Specialized pipeline management software focuses specifically on optimizing the sales process, providing features such as opportunity tracking, forecasting, and deal management. These tools offer real-time visibility into pipeline health, allowing sales managers to monitor progress, identify potential risks, and take proactive measures to ensure success.
Examples include Pipedrive, Close.io, and Insightly.
- Project Management Tools:While primarily designed for project management, tools like Asana, Trello, and Jira can also be effectively utilized for pipeline management, particularly for complex sales cycles involving multiple stakeholders and tasks. These tools enable teams to collaborate, track progress, and manage deadlines, ensuring that all necessary steps are taken to close deals.
Pipeline Optimization Methodologies and Techniques
Effective pipeline optimization involves implementing strategies and techniques that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process. This includes identifying and addressing bottlenecks, improving lead qualification, and streamlining workflows.
- Lead Scoring:This technique assigns numerical values to leads based on specific criteria, such as demographics, engagement levels, and purchase history. By prioritizing leads with higher scores, sales teams can focus their efforts on the most promising opportunities.
- Sales Process Automation:Automating repetitive tasks, such as email follow-ups and data entry, frees up sales representatives to focus on more strategic activities, like relationship building and deal negotiation.
- Sales Forecasting and Reporting:Regular forecasting and reporting provide valuable insights into pipeline health, allowing sales managers to identify trends, predict future performance, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and sales strategies.
- Pipeline Segmentation:Dividing the pipeline into different stages based on deal size, complexity, or other relevant factors enables sales teams to tailor their approach and allocate resources effectively.
- Sales Enablement:Providing sales representatives with the necessary training, tools, and resources to effectively manage their pipelines and close deals is crucial for pipeline optimization.
Comparison of Pipeline Management Frameworks
Different frameworks can be applied to manage sales pipelines, each with its unique characteristics and advantages.
- Agile Framework:Agile methodologies emphasize iterative development, continuous improvement, and flexibility. In a sales context, Agile principles can be applied to prioritize high-value leads, adapt to changing market conditions, and make quick adjustments to sales strategies.
- Waterfall Framework:The Waterfall framework follows a linear, sequential approach, with each stage completed before moving to the next. This approach is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and predictable timelines, but it can be less flexible in dynamic environments.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Data analysis is an essential component of pipeline management. By analyzing data from various stages of the sales pipeline, businesses can gain valuable insights into their sales processes, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize their sales performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are crucial for tracking and measuring the effectiveness of a sales pipeline. They provide quantifiable metrics that reflect the progress and performance of the pipeline.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into customers at each stage of the pipeline.
- Average Deal Size: The average value of deals closed.
- Lead Source Performance: The effectiveness of different lead generation sources in attracting qualified leads.
- Sales Cycle Length: The average time it takes to close a deal.
- Win Rate: The percentage of deals that are won.
- Pipeline Velocity: The speed at which leads move through the pipeline.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The total revenue generated from a customer over their lifetime.
Sample Report Structure
A well-structured report provides a comprehensive overview of pipeline progress and insights. Here’s a sample report structure that showcases key metrics and analyses:
Executive Summary
- A concise overview of the pipeline performance for the reporting period.
- Highlight key achievements and areas for improvement.
Pipeline Overview
- Pipeline Value: Total value of opportunities in the pipeline.
- Stage Distribution: Number of opportunities in each stage of the pipeline.
- Conversion Rates: Conversion rates for each stage of the pipeline.
Lead Source Performance
- Lead Source Breakdown: Number of leads generated from different sources.
- Lead Source Conversion Rates: Conversion rates for each lead source.
Sales Cycle Analysis
- Average Sales Cycle Length: Average time it takes to close a deal.
- Sales Cycle Length Distribution: Distribution of sales cycle lengths across different deals.
Deal Analysis
- Win Rate: Percentage of deals won.
- Average Deal Size: Average value of deals closed.
- Deal Stage Analysis: Analysis of deal progression at each stage.
Recommendations
- Based on the data analysis, provide recommendations for improving pipeline performance.
- Suggest strategies for optimizing lead generation, conversion rates, and sales cycle length.
Future Trends in Pipeline Management
The field of pipeline management is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for efficiency and optimization. Emerging trends are shaping the future of pipeline management, impacting how pipelines are designed, built, operated, and maintained.
Impact of Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and Data Analytics
Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics are transforming pipeline management by streamlining operations, improving decision-making, and enhancing safety and reliability. These technologies are playing a crucial role in optimizing pipeline performance and addressing challenges associated with aging infrastructure, environmental regulations, and workforce shortages.
- Automated Pipeline Monitoring and Control: Automation technologies enable real-time monitoring of pipeline systems, detecting anomalies and potential issues before they escalate. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from sensors and other sources to identify patterns and predict potential problems. This proactive approach helps prevent costly downtime and ensures the safe and efficient operation of pipelines.
- Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management: AI-powered predictive maintenance models can analyze historical data and identify patterns that indicate potential failures. By predicting equipment failures, pipeline operators can schedule maintenance proactively, reducing the risk of unexpected downtime and extending the lifespan of assets. This approach also optimizes maintenance schedules, minimizing costs and maximizing asset utilization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data analytics plays a vital role in pipeline management, providing insights that inform strategic decisions. By analyzing data from various sources, such as sensor readings, operational records, and environmental data, pipeline operators can identify areas for improvement, optimize pipeline performance, and make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and expansion.
Final Summary
From defining the stages of a pipeline to leveraging data analytics for informed decision-making, this exploration of pipeline management has highlighted the multifaceted nature of this crucial business function. By embracing best practices, incorporating innovative tools and techniques, and staying informed about emerging trends, organizations can harness the power of pipeline management to achieve operational excellence and drive sustainable growth.
Answers to Common Questions
What are some examples of pipeline management tools?
Popular pipeline management tools include Trello, Asana, Jira, and monday.com. These tools offer features for task management, project tracking, collaboration, and reporting.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my pipeline management system?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead conversion rate, average deal size, and pipeline velocity can help measure the effectiveness of your pipeline management system. Tracking these metrics provides insights into the efficiency and performance of your sales process.