Opportunity Management is the strategic process of identifying, evaluating, developing, and executing opportunities to achieve organizational goals. It involves a systematic approach to uncovering new avenues for growth, innovation, and competitive advantage.
From market trends and technological advancements to customer needs and internal capabilities, opportunity management helps businesses capitalize on potential while mitigating risks. It requires a deep understanding of the business environment, a structured framework for analysis, and a commitment to execution.
Defining Opportunity Management
Opportunity management is a strategic process that businesses use to identify, evaluate, and capitalize on potential opportunities for growth and improvement. It involves systematically seeking out new avenues for revenue generation, market expansion, and operational efficiency, while mitigating risks and maximizing returns.
The Key Components of a Successful Opportunity Management Framework
A robust opportunity management framework comprises several key components that work together to ensure effective identification, evaluation, and execution of opportunities.
- Opportunity Identification:This involves actively seeking out potential opportunities through market research, customer feedback, competitive analysis, and industry trends. The goal is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the landscape and identify potential areas for growth and improvement.
- Opportunity Evaluation:Once opportunities are identified, they must be carefully evaluated to assess their viability and potential impact. This includes considering factors such as market size, competition, regulatory environment, and resource requirements.
- Opportunity Prioritization:Given limited resources, it is essential to prioritize opportunities based on their potential impact, feasibility, and alignment with strategic goals. This involves ranking opportunities based on factors such as return on investment, time to market, and strategic importance.
- Opportunity Planning and Execution:Once prioritized, opportunities need to be carefully planned and executed. This includes developing detailed project plans, allocating resources, and establishing clear timelines and milestones. Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for successful execution.
- Opportunity Monitoring and Evaluation:Ongoing monitoring and evaluation are essential to track progress, identify potential challenges, and make necessary adjustments. This involves collecting data, analyzing performance, and making informed decisions based on the results.
The Role of Opportunity Management in Achieving Organizational Goals
Opportunity management plays a critical role in achieving organizational goals by providing a structured and systematic approach to identifying and capitalizing on potential growth opportunities.
- Revenue Growth:Opportunity management helps businesses identify new revenue streams, expand into new markets, and increase sales by targeting specific customer segments and developing innovative products or services.
- Market Leadership:By proactively identifying and capitalizing on emerging trends and opportunities, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and establish themselves as market leaders.
- Operational Efficiency:Opportunity management can lead to process improvements, cost reductions, and increased productivity by identifying areas for optimization and streamlining operations.
- Innovation and Growth:By fostering a culture of innovation and encouraging employees to identify and pursue new opportunities, businesses can drive growth and remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
Identifying and Evaluating Opportunities
Identifying and evaluating opportunities are crucial steps in the opportunity management process. This involves recognizing potential areas for growth, improvement, or expansion, and then assessing their viability and potential impact on the business.
Methods for Identifying Opportunities
The process of identifying potential opportunities can vary depending on the business environment and the industry. However, some common methods include:
- Market Research:Analyzing market trends, customer needs, and competitor activities can reveal gaps in the market or unmet needs that present opportunities for new products, services, or market segments. This involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as industry reports, customer surveys, and competitor analysis.
- Customer Feedback:Gathering feedback from existing and potential customers can provide valuable insights into their preferences, pain points, and unmet needs. This feedback can be collected through surveys, focus groups, social media monitoring, and customer support interactions.
- Internal Analysis:Examining the company’s internal strengths, weaknesses, resources, and capabilities can help identify opportunities for improvement or expansion. This involves analyzing operational processes, financial performance, and employee skills and expertise.
- Brainstorming and Innovation Sessions:Engaging employees in brainstorming and innovation sessions can generate creative ideas and solutions for new products, services, or business models. This encourages collaboration and open communication, leading to diverse perspectives and potential opportunities.
- Networking and Industry Events:Attending industry events, conferences, and networking opportunities can expose businesses to new trends, technologies, and potential partners. This provides a platform for learning about emerging opportunities and connecting with individuals who can offer valuable insights and connections.
Evaluating Opportunity Viability
Once potential opportunities are identified, it is crucial to evaluate their viability and potential impact. This involves assessing factors such as:
- Market Size and Growth:Determining the size and growth potential of the target market is essential to assess the opportunity’s long-term viability. A large and growing market provides a broader customer base and greater potential for revenue growth.
- Competitive Landscape:Analyzing the competitive landscape helps understand the level of competition and the potential for differentiation. Assessing the strengths and weaknesses of competitors can inform strategies for entering the market and achieving a competitive advantage.
- Financial Feasibility:Evaluating the financial feasibility of the opportunity involves assessing the costs associated with developing, launching, and marketing the product or service. This includes analyzing the potential return on investment (ROI) and the time frame for achieving profitability.
- Resource Availability:Determining whether the company has the necessary resources, including financial, human, and technological resources, to successfully pursue the opportunity is crucial. This involves assessing the availability of skilled personnel, capital, and infrastructure.
- Alignment with Business Strategy:Ensuring that the opportunity aligns with the company’s overall business strategy and goals is essential for long-term success. This involves evaluating whether the opportunity complements existing products or services, expands the customer base, or contributes to the company’s overall growth objectives.
Prioritizing and Selecting Opportunities
Once opportunities have been evaluated, it is important to prioritize and select the most promising ones for further exploration. This involves considering criteria such as:
- Potential Impact:The potential impact of the opportunity on the company’s revenue, market share, or brand reputation is a key factor in prioritization. Opportunities with the highest potential impact are typically given higher priority.
- Risk Level:The level of risk associated with pursuing the opportunity is another important consideration. Opportunities with lower risk levels are generally preferred, as they offer a greater likelihood of success.
- Time Frame:The time frame required to develop, launch, and achieve profitability for the opportunity is also a factor. Opportunities with shorter time frames are often more appealing, as they provide faster returns on investment.
- Resource Requirements:The resources required to pursue the opportunity, including financial, human, and technological resources, are taken into account. Opportunities that require fewer resources are generally more feasible and easier to implement.
- Alignment with Company Values:The opportunity’s alignment with the company’s values, mission, and vision is essential for ensuring long-term success. Opportunities that are consistent with the company’s core principles are more likely to be embraced by stakeholders and employees.
Opportunity Development and Execution: Opportunity Management
Once opportunities have been identified and evaluated, the next crucial step is developing and executing a comprehensive plan to maximize their potential. This involves translating the initial assessment into actionable strategies, allocating resources effectively, and engaging stakeholders to drive successful implementation.
Developing a Comprehensive Opportunity Plan
A well-structured opportunity plan serves as a roadmap for achieving desired outcomes. It Artikels the specific actions, timelines, and resources required to capitalize on the opportunity. The development process typically involves the following steps:
- Define Clear Objectives:Clearly articulate the desired outcomes and specific goals that the opportunity aims to achieve. This provides a clear direction for the plan and ensures everyone involved understands the ultimate purpose.
- Develop Actionable Strategies:Artikel the specific steps and tactics that will be employed to achieve the objectives. This includes identifying key activities, tasks, and milestones that need to be accomplished.
- Allocate Resources Effectively:Determine the necessary resources, including financial, human, and technological, to support the implementation of the plan. Ensure resources are allocated strategically to maximize efficiency and impact.
- Establish Timelines and Milestones:Define clear deadlines and milestones for each stage of the opportunity development and execution process. This helps track progress, manage expectations, and ensure timely completion.
- Identify and Address Potential Risks:Proactively identify potential risks and challenges that could hinder the success of the opportunity. Develop mitigation strategies to minimize their impact and ensure the plan remains on track.
- Develop a Monitoring and Evaluation Framework:Establish mechanisms to track progress, measure outcomes, and evaluate the effectiveness of the plan. This allows for continuous improvement and adjustments based on real-time data.
Resource Allocation and Stakeholder Engagement
Effective resource allocation and stakeholder engagement are essential for successful opportunity execution.
- Resource Allocation:Strategic allocation of resources ensures that the right resources are available at the right time to support the implementation of the plan. This includes allocating financial resources, assigning personnel with relevant skills, and providing access to necessary tools and technologies.
- Stakeholder Engagement:Engaging stakeholders throughout the opportunity development and execution process is crucial for building consensus, fostering collaboration, and ensuring buy-in. This involves actively communicating with stakeholders, seeking their input, and addressing their concerns.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks and Maximizing Potential
Opportunities often present inherent risks that need to be addressed to maximize their potential. Strategies for mitigating risks and maximizing the potential of opportunities include:
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation:Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. Develop contingency plans and mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of risks.
- Scenario Planning:Explore different scenarios and potential outcomes to develop flexible and adaptable plans. This allows for adjustments based on changing circumstances and unforeseen events.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation:Regularly monitor progress, measure outcomes, and evaluate the effectiveness of the plan. This allows for early identification of issues and adjustments to ensure the opportunity remains on track.
- Adaptability and Innovation:Be open to adapting the plan and exploring new approaches as needed. Embrace innovation and creative solutions to overcome challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Opportunity Management Tools and Technologies
Effective opportunity management relies on robust tools and technologies that streamline processes, enhance analysis, and ultimately contribute to better decision-making. These tools provide a centralized platform for tracking opportunities, managing communication, and analyzing performance data, thereby maximizing the potential of each opportunity.
Software Tools and Technologies for Opportunity Management
Various software tools and technologies are available to support opportunity management. These tools can be categorized based on their functionality and target audience.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems:CRMs are comprehensive platforms that manage customer interactions and data. They often include opportunity management modules that allow users to track leads, opportunities, and sales pipelines. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and HubSpot.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA) Tools:SFA tools are designed specifically for sales teams and provide features for opportunity tracking, pipeline management, forecasting, and reporting. Examples include Pipedrive, Zoho CRM, and Close.io.
- Project Management Software:Project management tools, such as Asana, Trello, and Jira, can be used to manage the execution and delivery of opportunities. They provide features for task management, collaboration, and progress tracking.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics Tools:BI tools, like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense, offer data visualization and analysis capabilities. They can be used to analyze opportunity performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Enhancing Efficiency and Effectiveness
Opportunity management tools offer several benefits that enhance efficiency and effectiveness:
- Centralized Data Management:Tools provide a single source of truth for opportunity data, eliminating the need for manual tracking and reducing the risk of errors.
- Automated Processes:Automation features, such as lead scoring, pipeline management, and reporting, save time and resources, allowing teams to focus on higher-value activities.
- Improved Collaboration:Tools facilitate collaboration among team members by providing shared access to data, communication channels, and task management features.
- Enhanced Analysis and Reporting:Tools offer data visualization and reporting capabilities that provide insights into opportunity performance, allowing teams to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions.
Comparison of Opportunity Management Platforms
| Feature | Salesforce | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | HubSpot | Pipedrive | Zoho CRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
| Target Audience | Large enterprises, mid-sized businesses | Large enterprises, mid-sized businesses | Small businesses, startups | Small businesses, startups | Small businesses, startups |
| Features | CRM, sales automation, marketing automation, service management | CRM, sales automation, marketing automation, service management | CRM, sales automation, marketing automation, email marketing | Sales automation, pipeline management, forecasting | CRM, sales automation, marketing automation, customer support |
| Integration | Integrates with various third-party apps | Integrates with various third-party apps | Integrates with various third-party apps | Integrates with various third-party apps | Integrates with various third-party apps |
| Mobile Access | Mobile app available | Mobile app available | Mobile app available | Mobile app available | Mobile app available |
Best Practices in Opportunity Management
Effective opportunity management is crucial for organizations seeking to achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage. It involves a structured and strategic approach to identifying, evaluating, developing, and executing opportunities that align with organizational goals. This section explores best practices to foster a robust opportunity management culture and optimize processes for success.
Establishing a Robust Opportunity Management Culture
A thriving opportunity management culture requires a strong foundation of leadership commitment, employee engagement, and a data-driven approach. This culture encourages a proactive mindset, fostering a continuous search for opportunities and innovative solutions.
- Leadership Buy-in:Strong leadership commitment is paramount. Leaders must champion opportunity management, allocate resources, and provide clear expectations. They should actively participate in identifying and prioritizing opportunities, demonstrating their commitment to the process.
- Employee Empowerment:Empower employees at all levels to identify and propose opportunities. Encourage a culture of open communication and collaboration, where ideas are welcomed and explored. Provide training and tools to equip employees with the skills needed to effectively manage opportunities.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:Utilize data and analytics to inform opportunity evaluation, prioritization, and resource allocation. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of opportunity management initiatives and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:Establish a culture of continuous improvement. Regularly review and refine opportunity management processes to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Encourage feedback from employees and stakeholders to identify areas for optimization.
Examples of Successful Opportunity Management Initiatives
Several organizations have successfully implemented opportunity management initiatives, leading to significant business outcomes.
- Example 1:A leading technology company implemented a centralized opportunity management system, enabling them to track and manage opportunities across various departments. This system provided real-time visibility into the pipeline, allowing for more efficient resource allocation and improved forecasting. Key takeaways include the importance of data-driven decision making and the need for a centralized system to ensure consistency and transparency.
- Example 2:A retail chain implemented a customer-centric opportunity management approach, focusing on identifying and addressing customer needs. They conducted market research, analyzed customer feedback, and leveraged social media insights to identify emerging trends and opportunities. This initiative resulted in increased customer satisfaction, higher sales, and a stronger brand reputation.
Recommendations for Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Continuous improvement is essential to maximize the effectiveness of opportunity management. Here are some recommendations for optimizing processes:
- Regularly Review and Update Processes:Conduct periodic reviews of opportunity management processes to ensure they remain aligned with evolving business needs and market conditions. Update processes based on feedback from employees, stakeholders, and performance data.
- Utilize Technology:Leverage opportunity management software and tools to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and improve data analysis capabilities. These technologies can provide valuable insights, improve collaboration, and enhance decision-making.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation:Encourage employees to think outside the box and explore new opportunities. Create a space for experimentation and learning, where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and taking calculated risks.
- Measure and Track Results:Establish clear KPIs to measure the success of opportunity management initiatives. Regularly track progress and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows for continuous optimization and ensures that efforts are aligned with organizational goals.
Case Studies in Opportunity Management
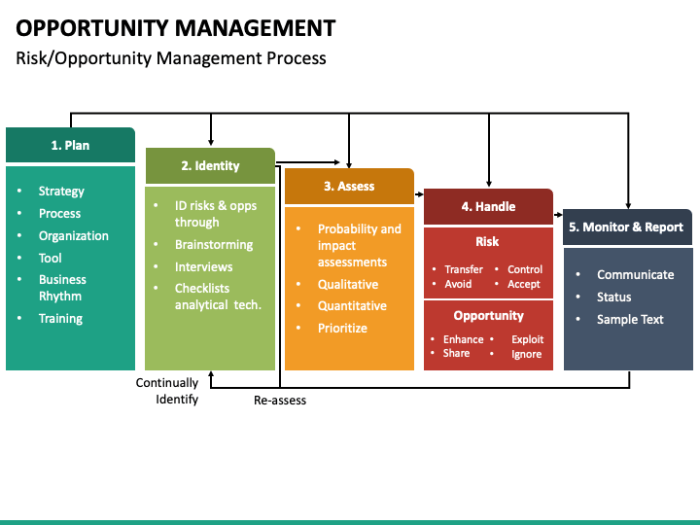
Examining real-world scenarios provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of opportunity management strategies. By analyzing successful and unsuccessful cases, we can glean practical lessons and identify key factors that contribute to their outcomes. These case studies serve as a roadmap for organizations to implement effective opportunity management practices and avoid common pitfalls.
Case Study 1: Salesforce’s Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Salesforce, a leading CRM software provider, has consistently demonstrated effective opportunity management practices. Their success can be attributed to several key factors:
- Data-Driven Approach:Salesforce leverages extensive data analytics to identify potential opportunities, analyze customer behavior, and tailor sales strategies. This data-driven approach enables them to make informed decisions and prioritize opportunities based on their likelihood of success.
- Automated Opportunity Management Processes:Salesforce has implemented automated workflows and systems for managing opportunities throughout their lifecycle. This automation streamlines processes, reduces manual effort, and ensures consistent execution.
- Strong Sales Team Collaboration:Salesforce fosters a collaborative environment among their sales team, encouraging information sharing and knowledge transfer. This collective approach allows them to leverage the expertise of various team members and effectively manage complex opportunities.
Case Study 2: Tesla’s Electric Vehicle Innovation
Tesla’s remarkable success in the electric vehicle market is a testament to their innovative opportunity management strategy. Key factors contributing to their success include:
- Early Identification of Emerging Trends:Tesla recognized the potential of electric vehicles early on and invested heavily in research and development, creating a first-mover advantage in the market.
- Strategic Partnerships:Tesla has forged strategic partnerships with key players in the automotive industry, leveraging their expertise and resources to accelerate their growth and market penetration.
- Customer-Centric Approach:Tesla prioritizes customer satisfaction and continuously seeks feedback to improve their products and services. This customer-centric approach has fostered brand loyalty and strong word-of-mouth marketing.
Case Study 3: Kodak’s Failure to Adapt to Digital Photography, Opportunity Management
Kodak, once a dominant player in the film photography industry, failed to adapt to the rise of digital photography. This case study highlights the importance of recognizing and responding to changing market dynamics.
- Resistance to Innovation:Kodak initially dismissed the threat posed by digital photography, clinging to its traditional film-based business model. This resistance to innovation ultimately led to their downfall.
- Lack of Strategic Planning:Kodak failed to develop a comprehensive strategy for navigating the transition to digital photography. They missed opportunities to invest in and develop digital technologies.
- Inability to Adapt:Despite recognizing the shift in the market, Kodak struggled to adapt its business model and operations to the new digital landscape. This inability to adapt ultimately resulted in their decline.
Last Recap
By implementing a robust opportunity management system, organizations can unlock new possibilities, drive sustainable growth, and stay ahead of the competition. This comprehensive approach ensures that every opportunity is carefully considered, prioritized, and pursued with the resources and expertise needed for success.
User Queries
What are some common examples of opportunities in business?
Opportunities can range from expanding into new markets or product lines to developing strategic partnerships or adopting new technologies. They can also involve optimizing existing processes, improving customer service, or enhancing brand awareness.
How can I measure the success of an opportunity management program?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) can be used to measure the effectiveness of opportunity management, such as revenue growth, market share gains, customer satisfaction, and return on investment (ROI).
What are some challenges associated with opportunity management?
Challenges can include identifying and prioritizing opportunities, securing resources, managing stakeholders, and adapting to changing market conditions.