CRM Strategy is the cornerstone of building strong, lasting relationships with your customers. It’s not just about managing contacts; it’s about understanding your customers’ needs, anticipating their desires, and delivering exceptional experiences at every touchpoint. This strategy involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses customer segmentation, relationship management processes, technology utilization, and continuous measurement and improvement.
From defining clear objectives that align with your business goals to leveraging cutting-edge technology like AI and omnichannel marketing, a well-defined CRM strategy empowers businesses to cultivate customer loyalty, drive revenue growth, and establish a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Defining CRM Strategy
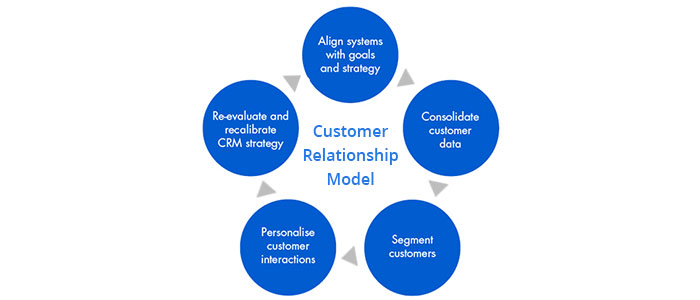
A CRM strategy is a comprehensive plan that Artikels how an organization will use customer relationship management (CRM) tools and processes to improve customer interactions, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive business growth. It encompasses various aspects, from defining target customer segments and understanding their needs to implementing specific CRM solutions and measuring the effectiveness of the strategy.
Core Objectives of a CRM Strategy
The core objectives of a CRM strategy are directly aligned with overall business goals. The primary aim is to build and maintain strong, long-lasting relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and advocacy. This can be achieved by:
- Improving Customer Acquisition:A well-defined CRM strategy can help identify potential customers, target them effectively, and convert them into paying customers. This can be done through personalized marketing campaigns, targeted promotions, and effective lead nurturing strategies.
- Enhancing Customer Retention:CRM strategies focus on understanding customer needs and preferences, providing excellent customer service, and delivering personalized experiences. This helps reduce churn rates and build lasting relationships with customers.
- Increasing Customer Lifetime Value:By focusing on customer satisfaction and loyalty, CRM strategies can increase the average revenue generated per customer over time. This can be achieved by encouraging repeat purchases, upselling, and cross-selling products and services.
- Improving Operational Efficiency:CRM solutions can automate various tasks, such as lead management, sales forecasting, and customer support, improving efficiency and freeing up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Gaining Valuable Insights:CRM systems collect and analyze data on customer interactions, providing valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This data can be used to optimize marketing campaigns, improve product development, and enhance customer service.
Key Stakeholders Involved in CRM Strategy Development and Implementation
Developing and implementing a successful CRM strategy requires collaboration and input from various stakeholders across the organization. Key stakeholders include:
- Executive Management:They provide strategic direction and resources for the CRM initiative, ensuring alignment with overall business goals.
- Sales and Marketing Teams:These teams are directly responsible for customer interactions and need to be actively involved in defining CRM processes and using CRM tools to optimize their efforts.
- Customer Service Team:The customer service team plays a crucial role in delivering excellent customer experiences and needs to be equipped with the right CRM tools and training to effectively handle customer inquiries and issues.
- IT Department:The IT department is responsible for implementing, maintaining, and integrating the CRM system with other business systems.
- Data Analysts and Business Intelligence Professionals:They are responsible for analyzing CRM data to identify trends, insights, and opportunities for improvement.
Importance of Data Integration and Data Quality in a CRM Strategy
Data is the lifeblood of a CRM strategy. Integrating data from various sources and ensuring its quality is essential for a successful implementation.
- Data Integration:Integrating data from different sources, such as marketing automation platforms, sales management systems, and customer support databases, creates a single, unified view of the customer. This holistic view enables a deeper understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs, leading to more effective marketing campaigns, personalized customer experiences, and improved decision-making.
- Data Quality:Accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for a successful CRM strategy. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights, ineffective marketing campaigns, and inefficient customer service. Ensuring data accuracy and completeness requires regular data cleansing, validation, and ongoing monitoring to maintain data integrity.
Customer Segmentation and Targeting: CRM Strategy
Customer segmentation and targeting are crucial elements of a successful CRM strategy. By dividing your customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, you can tailor your CRM initiatives to meet their specific needs and preferences, leading to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, profitability.
Customer Segmentation Strategies
Customer segmentation involves grouping customers into distinct segments based on shared characteristics. This allows businesses to tailor their marketing and sales efforts to each segment, leading to more effective campaigns and improved customer relationships. Here are some common customer segmentation strategies:
- Demographic Segmentation:This strategy divides customers based on factors such as age, gender, location, income, and education level. For example, a clothing retailer might segment its customers based on age to offer targeted promotions for different age groups.
- Psychographic Segmentation:This strategy focuses on customers’ psychological characteristics, including their values, beliefs, lifestyle, and interests. For instance, a travel agency might segment its customers based on their travel preferences, such as adventure, luxury, or family-oriented trips.
- Behavioral Segmentation:This strategy considers customers’ purchasing behavior, such as their purchase history, frequency, and spending patterns. An online retailer could segment customers based on their purchase history to offer personalized product recommendations.
- Needs-Based Segmentation:This strategy groups customers based on their specific needs and wants. For example, a software company might segment its customers based on their business requirements, such as accounting, marketing, or customer service needs.
Tailoring CRM Initiatives to Customer Segments
Once you have segmented your customers, you can tailor your CRM initiatives to each segment’s unique characteristics. This includes:
- Personalized Communication:Delivering personalized messages and offers based on customer preferences and behavior can significantly enhance customer engagement and loyalty. For example, a retail store can send personalized emails promoting products based on a customer’s past purchases or browsing history.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns:Design marketing campaigns specifically tailored to the interests and needs of each customer segment. This ensures that marketing messages are relevant and resonate with the target audience. For example, a financial institution could offer targeted investment products based on a customer’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Customer Support and Service:Provide tailored support and service experiences based on customer segment needs. For example, a software company can offer dedicated support channels for enterprise customers with complex requirements.
Effective Customer Targeting Methods within a CRM Framework
Effective customer targeting involves identifying and reaching out to the most valuable customers within each segment. Here are some effective methods:
- Predictive Analytics:Utilize predictive models to identify customers with a high probability of making a purchase or becoming loyal customers. This can help prioritize marketing efforts and allocate resources efficiently. For example, a telecommunications company can use predictive models to identify customers at risk of churn and offer them targeted retention offers.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV):Calculate the estimated value of each customer over their lifetime with your business. This metric helps prioritize customers with higher potential value and focus on building long-term relationships. For example, an e-commerce platform can use CLTV to identify high-value customers and offer them exclusive benefits and personalized experiences.
- Marketing Automation:Utilize marketing automation tools to automate targeted communication and campaigns across multiple channels, such as email, SMS, and social media. This allows for efficient and personalized outreach to different customer segments. For example, a travel agency can use marketing automation to send personalized email campaigns promoting travel deals based on a customer’s previous bookings and interests.
Customer Relationship Management Processes
Customer relationship management (CRM) processes are the strategies and actions a business uses to manage its interactions with customers across the entire customer lifecycle. A well-defined CRM process ensures that customers have positive experiences, builds loyalty, and drives revenue growth.
Optimizing Customer Lifecycle Stages with CRM
CRM plays a crucial role in optimizing each stage of the customer lifecycle. Here’s how:
- Awareness:CRM tools can be used to create targeted marketing campaigns that reach potential customers at the awareness stage. These campaigns can be based on demographics, interests, and behaviors. For example, a company selling fitness trackers could use CRM to target individuals who are interested in health and wellness, have recently searched for fitness trackers online, or have visited fitness-related websites.
- Consideration:During the consideration stage, potential customers are researching different options and comparing products or services. CRM can be used to provide valuable information and resources to help customers make informed decisions. For instance, a CRM system could track website visits and provide personalized product recommendations based on browsing history.
- Decision:At the decision stage, customers are ready to make a purchase. CRM can be used to streamline the purchasing process, provide incentives, and offer personalized offers. For example, a company selling software could offer a free trial or discount to customers who are ready to make a purchase.
- Retention:Once a customer has made a purchase, CRM can be used to nurture the relationship and encourage repeat business. This includes providing excellent customer service, offering personalized recommendations, and creating loyalty programs. For instance, a company selling clothing could use CRM to send personalized emails with exclusive offers to loyal customers.
- Advocacy:The final stage of the customer lifecycle is advocacy. CRM can be used to encourage customers to become brand advocates and share their positive experiences with others. For example, a company could offer incentives to customers who refer new customers to the business.
Leveraging CRM for Lead Generation, Nurturing, and Conversion
CRM tools can be effectively leveraged to generate leads, nurture them, and ultimately convert them into paying customers.
- Lead Generation:CRM systems can be used to capture leads through various channels, such as website forms, social media campaigns, and email marketing. By integrating with marketing automation platforms, CRM can automate lead capture and qualification processes.
- Lead Nurturing:Once leads are captured, CRM tools can be used to nurture them through personalized communication and targeted content. This includes sending relevant emails, providing valuable resources, and engaging with leads on social media. For instance, a CRM system can track website activity and send emails with relevant content based on pages visited.
- Lead Conversion:CRM can help convert leads into paying customers by providing sales teams with the necessary information and tools. This includes tracking lead interactions, providing insights into lead behavior, and automating sales processes. For example, a CRM system can provide sales reps with a comprehensive view of a lead’s history, including interactions with marketing materials and previous conversations.
Managing Customer Interactions and Resolving Issues
CRM systems provide a centralized platform for managing customer interactions and resolving issues effectively.
- Customer Support:CRM tools can be used to manage customer support inquiries, track issues, and provide timely resolutions. This includes features such as ticketing systems, live chat, and knowledge bases. For example, a CRM system can track customer support tickets, assign them to appropriate agents, and provide a history of interactions.
- Issue Resolution:CRM can help resolve customer issues efficiently by providing access to relevant information, tracking progress, and ensuring communication transparency. For instance, a CRM system can track the status of customer complaints, provide insights into common issues, and automate follow-up communications.
- Customer Feedback:CRM systems can be used to collect customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media monitoring. This feedback can be used to improve products, services, and customer experiences. For example, a CRM system can collect customer feedback through surveys and provide insights into areas for improvement.
CRM Technology and Tools
A well-defined CRM strategy requires robust technology and tools to implement and manage customer relationships effectively. CRM platforms provide a centralized system for managing customer data, interactions, and processes, enabling businesses to streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive revenue growth.
Comparison of CRM Platforms
Choosing the right CRM platform is crucial for a successful strategy. Different platforms offer varying features, functionalities, and pricing models. Understanding these differences is essential to selecting the platform that best suits your specific business needs.
- Features and Functionalities: Consider features such as contact management, lead management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer support, reporting and analytics, and integration with other business systems. Some platforms are designed for specific industries or business sizes, while others offer a more comprehensive suite of tools.
- Pricing: CRM platforms offer various pricing models, including subscription-based, usage-based, and tiered pricing. The cost can vary based on the number of users, features, and functionalities included. It’s essential to evaluate the pricing structure and ensure it aligns with your budget.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is crucial for adoption and success. Look for platforms with intuitive navigation, customizable dashboards, and comprehensive training resources. Consider the platform’s scalability and ability to adapt to your evolving business needs.
Integration with Other Business Systems
CRM platforms should seamlessly integrate with other business systems, such as marketing automation, e-commerce, accounting, and customer support systems. This integration allows for a holistic view of customer interactions across all touchpoints and enables businesses to automate workflows and streamline processes.
For example, integrating a CRM with an e-commerce platform can provide valuable insights into customer purchasing behavior, allowing businesses to personalize marketing campaigns and offer targeted promotions.
Mobile CRM
Mobile CRM solutions empower businesses to engage with customers on the go. Mobile apps allow sales representatives to access customer data, manage leads, track opportunities, and provide real-time support, regardless of location. This accessibility enhances customer engagement and improves productivity.
Mobile CRM can also be used to gather customer feedback, conduct surveys, and provide personalized offers, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Measuring and Evaluating CRM Success
A robust CRM strategy goes beyond implementation; it demands continuous evaluation to ensure its effectiveness in achieving business goals. Measuring and evaluating CRM success is crucial for identifying areas for improvement, optimizing processes, and maximizing return on investment.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for CRM Success
Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide quantifiable metrics to track the progress and effectiveness of your CRM strategy. By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can gain insights into customer behavior, engagement, and satisfaction.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC):This metric reflects the average cost incurred to acquire a new customer. A lower CAC indicates efficient marketing and sales efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV):CLTV represents the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with your business. A higher CLTV indicates customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
- Customer Churn Rate:This metric measures the percentage of customers who stop doing business with you over a specific period. A lower churn rate signifies customer satisfaction and retention.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score:CSAT surveys measure customer satisfaction with specific interactions, products, or services. A high CSAT score indicates positive customer experiences.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS):NPS surveys gauge customer loyalty and willingness to recommend your brand. A higher NPS score reflects strong brand advocacy.
- Conversion Rate:This metric tracks the percentage of website visitors or leads who convert into customers. A higher conversion rate signifies effective marketing and sales strategies.
- Average Order Value (AOV):AOV measures the average amount spent by customers per transaction. A higher AOV indicates successful upselling and cross-selling efforts.
- Customer Engagement Rate:This metric measures the level of customer interaction with your brand across various channels, including email, social media, and website. Higher engagement indicates strong brand awareness and customer interest.
Tracking and Analyzing CRM Data
Tracking and analyzing CRM data is essential for gaining valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
- CRM Analytics Dashboards:Most CRM platforms offer built-in analytics dashboards that provide real-time insights into key performance indicators. These dashboards visualize data trends and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
- Customer Segmentation and Targeting:Analyzing CRM data allows for segmenting customers based on demographics, purchase history, and engagement levels. This segmentation enables targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences.
- Customer Journey Mapping:By tracking customer interactions across different touchpoints, businesses can map the customer journey and identify areas for improvement. This analysis helps optimize the customer experience and address pain points.
- A/B Testing:A/B testing allows businesses to experiment with different marketing messages, website designs, or email campaigns to determine the most effective strategies. Analyzing the results of A/B tests provides valuable data for optimizing marketing efforts and improving customer engagement.
Using CRM Insights to Optimize Processes and Improve Customer Experiences, CRM Strategy
CRM insights can be leveraged to optimize business processes and enhance customer experiences.
- Personalized Marketing Campaigns:By analyzing customer data, businesses can personalize marketing messages and offers based on individual preferences and purchase history. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of customer engagement and conversion.
- Proactive Customer Service:CRM data can help identify customers who are at risk of churn or experiencing issues. This information allows for proactive customer service interventions, preventing churn and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Improved Sales Processes:CRM data can provide insights into sales performance, identifying areas for improvement. This analysis helps optimize sales processes, streamline workflows, and increase sales efficiency.
- Product Development:Customer feedback and purchase history data can inform product development decisions. This data helps businesses understand customer needs and preferences, enabling them to create products that resonate with their target audience.
Future Trends in CRM
The landscape of customer relationship management (CRM) is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations. As we move forward, several trends are poised to shape the future of CRM, transforming how businesses interact with their customers.
Impact of AI and ML on CRM
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing CRM by automating tasks, providing insights, and personalizing customer interactions.
- AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
- ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling businesses to anticipate needs and personalize offers.
- AI-driven CRM systems can automate tasks like lead scoring, segmentation, and campaign optimization, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
For example, Amazon leverages AI to personalize product recommendations and predict customer needs, resulting in a highly tailored shopping experience.
The Rise of CXM in CRM Strategies
Customer experience management (CXM) is becoming increasingly crucial in CRM strategies as businesses recognize the importance of creating seamless and memorable customer journeys.
- CRM systems are integrating with CXM platforms to provide a holistic view of customer interactions across all touchpoints.
- Businesses are focusing on creating personalized experiences, addressing customer pain points, and building lasting relationships.
- Data analysis plays a vital role in CXM, enabling businesses to understand customer preferences, measure satisfaction, and identify areas for improvement.
Companies like Apple prioritize CXM, offering exceptional customer service, intuitive product design, and seamless integration across devices.
Omnichannel Marketing and CRM Transformation
Omnichannel marketing, which provides a consistent customer experience across all channels, is transforming CRM by connecting the dots between online and offline interactions.
- CRM systems are evolving to support omnichannel strategies, enabling businesses to track customer journeys across multiple touchpoints, including websites, mobile apps, social media, and physical stores.
- Businesses are using omnichannel marketing to personalize communication, offer targeted promotions, and provide seamless customer service regardless of the channel.
- Data integration is crucial for omnichannel CRM, allowing businesses to gather insights from all customer interactions and deliver a unified experience.
Starbucks, for instance, uses omnichannel marketing to personalize offers based on customer preferences, track loyalty program points, and provide consistent service across its mobile app, website, and physical stores.
Epilogue
By embracing a customer-centric approach and implementing a robust CRM strategy, businesses can unlock the true potential of their customer relationships. Through data-driven insights, personalized interactions, and continuous optimization, organizations can transform customer experiences, foster brand advocacy, and achieve sustainable growth in the long run.
The journey towards customer success starts with a clear CRM strategy, and the rewards are well worth the investment.
FAQ Section
What are some common challenges businesses face when implementing a CRM strategy?
Common challenges include data quality issues, resistance to change from employees, choosing the right CRM platform, and integrating CRM with existing systems. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, effective communication, and ongoing support.
How can I measure the success of my CRM strategy?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) to track include customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, customer satisfaction scores, conversion rates, and retention rates. Regular analysis of these metrics provides valuable insights for optimizing the CRM strategy.
What are some tips for choosing the right CRM platform for my business?
Consider factors such as your budget, business size, industry, specific requirements, and integration capabilities. Research different platforms, read reviews, and request demos to find the best fit for your needs.